Summary of a presentation about a model based on an elastic solid
Motivation
Basically I just always wante o know how, *exactly*, magnets work 🙂 (and why c is constant and of course, what spin 1/2 is)

A big problem is of course QM with all the various interpretations…
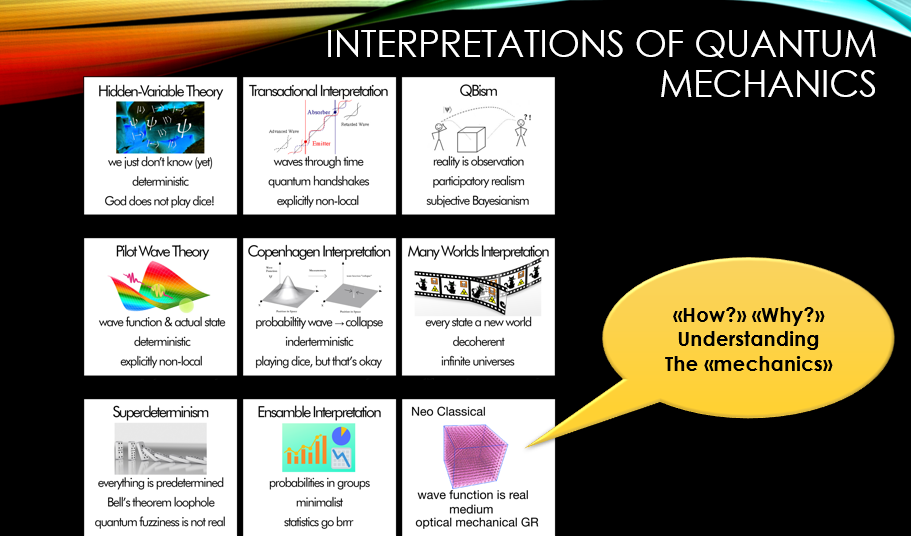
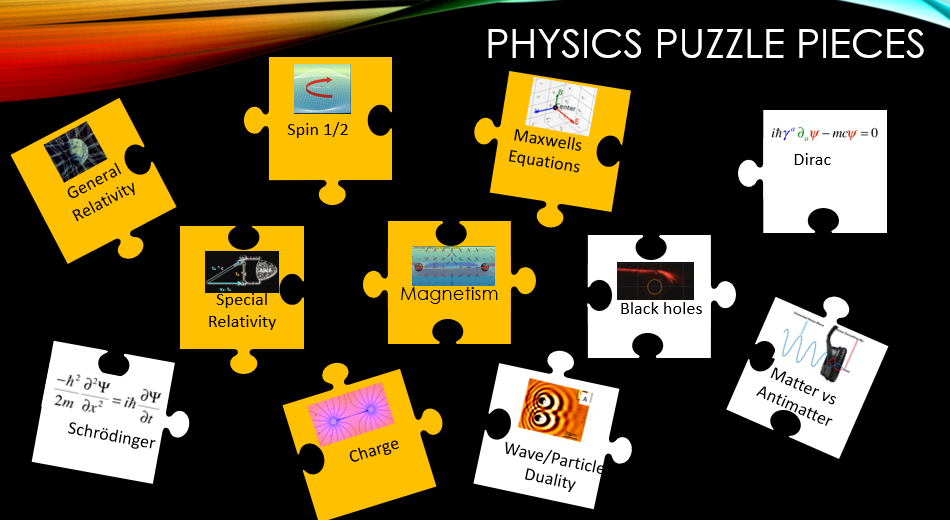
No matter what solution we come up with, the point is that all the various puzzle pieces have to fit together. That includes all these topics ranging from special relativity to general relativity to spin 1/2 etc etc.
| Phenomenon | “Mainstream” No Medium (Vacuum) | Elastic Solid |
| Special Relativity | ✅ Works, non-intuitive | ✅ Intuitive (wave speed) |
| General Relativity | ✅ Abstract curvature | ✅ Intuitive refraction (density gradient) |
| Quantum Mechanics | ✅ Abstract/probabilistic | ✅ Real physical waves |
| Spin-½ (Dirac) | ⚠️ Abstract spin-½ (720°) | ✅ Mechanical oscillation (spinor, belt trick) |
| Electromagnetism | ✅ Abstract fields | ✅ Fields as elastic vibrations |
| Matter/Antimatter | ⚠️ Abstract annihilation | ✅ Wave/anti-wave interference |
| Constant speed c | ⚠️ Postulated | ✅ Natural fixed wave speed |
| Preferred Frame? | ✅ No frame | ⚠️ Exists, undetectable |
That is why I will attempt to address most of these topics below:
General Relativity
Even Einstein thought that space must be “real” and be “rigid”:
“More careful reflection teaches us however, that the special theory of relativity does not compel us to deny ether. We may assume the existence of an ether; only we must give up ascribing a definite state of motion to it”
“Recapitulating, we may say that according to the general theory of relativity space is endowed with physical qualities; in this sense, therefore, there exists an ether.
According to the general theory of relativity space without ether is unthinkable;
for in such space there not only would be no propagation of light, but also no possibility of existence for standards of space and time (measuring-rods and clocks), nor therefore any space-time intervals in the physical sense”
I. Newton
Qu 19x (rewritten)
Doth not the Refraction of Light proceed from the different density of this Aetherial Medium in different places, the Light receding always from the [rarer] parts of the Medium? And is not the density thereof [less] in free and open spaces void of Air and other grosser Bodies
Qu. 21x (rewritten)
Is not this Medium much [denser] within the dense Bodies of the Sun, Stars, Planets and Comets, than in the empty Celestial spaces between them?
……
And though this [Decrease] of density may at great distances be exceeding slow, yet is the elastick force of this Medium be exceeding great, it may suffice to impel Bodies from the [rarer] parts of the medium towards the [denser], with all that power which we call Gravity. …
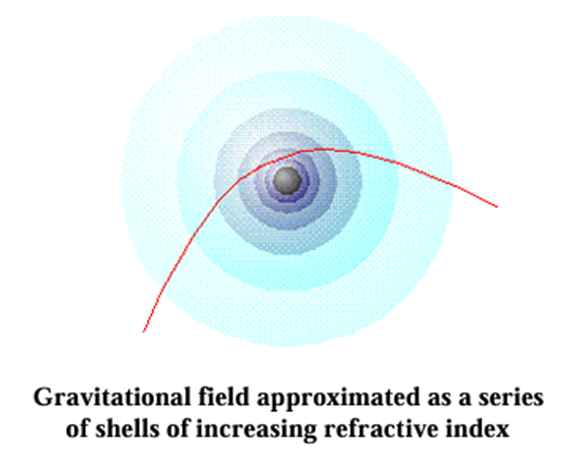
Baird, E. (2000). Newton’s Aether Model. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/pdf/physics/0011003
Hagen Kleinert:
Hagen Kleinert’s showed it is equivalent to Minkowski
3 spatial + 1 «density» dimension
It is the «fabric of space-(time)»
Optical-mechanical analogy to GR (refraction)
The solid can be deformed in an elastic way
Matter and light are waves
H. Kleinert, Gravity as Theory of Defects in a Crystal with Only Second-Gradient Elasticity, Annalen der Physik, Bd. 44, 1987, S. 117,
M. Danielewski, 2007, Z. Naturforsch. 62a, 564, The Planck – Kleinert Crystal

Instead of the metric tensor g, we can use a density function (a plastic gauge field):
Hagen Kleinerts “trick”:
•Euclidean coordinate system x plus
density function
• Is the siffness or density of the elastic solid
• Refraction: waves in an inhomogeneus medium bend:
Simulation: https://jsfiddle.net/Chenopdodium/n879e5dh/38/
Special Relativity

Medium | Density (ρ) kg/m³ | Stiffness (Bulk Modulus B) GPa | Wave Speed (c=sqrt(B/ρ) ) m/s |
| Air | ~1.2 | ~0.0001 | ~300 |
| Water | 1000 | 2 | ~1400 |
| Diamond | 3500 | ~440 | ~12,000 |
| Vacuum (Space) | ? (Unknown) | Very high (Elastic solid analogy) | 3*10^8 (light speed) |
•All you need to know is: The speed of a wave is constant in a medium

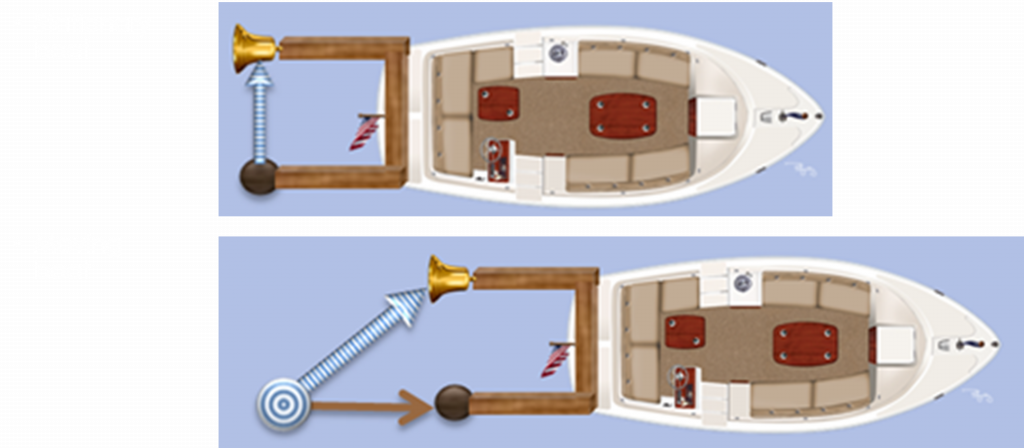
Moving clicks tick more slowly because the wave has to travel a longer path:
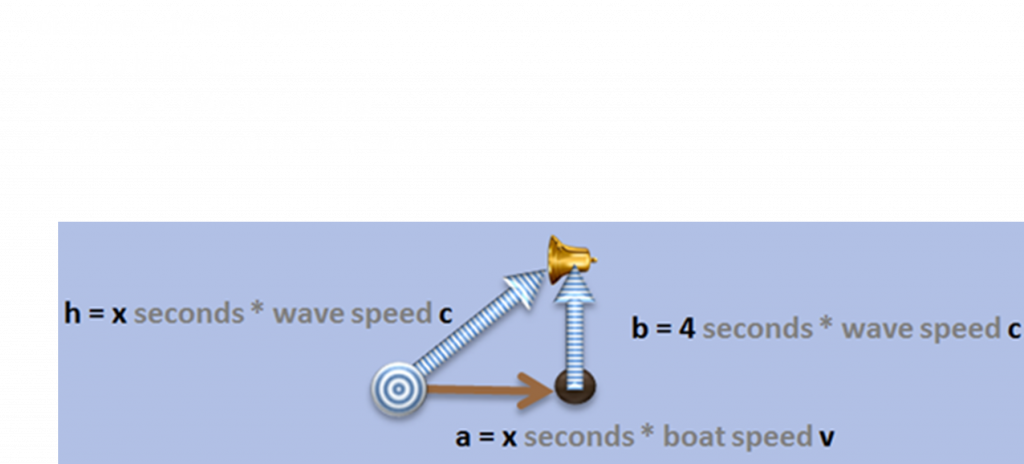


Simulation: https://jsfiddle.net/Chenopdodium/nxpagswk/
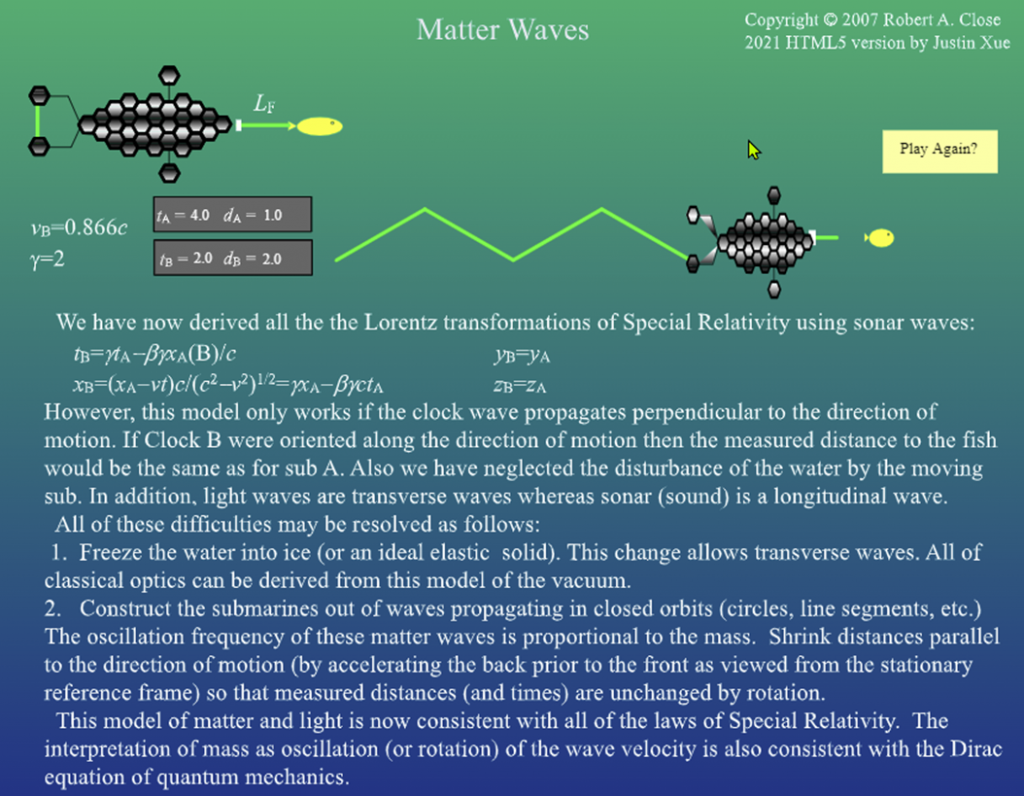
Also check out this simulation by Robert Close:
•https://www.classicalmatter.org/Physics/UnderwaterRelativity/HTML5/MatterWaves.html
Electromagnetic Potential/Maxwell
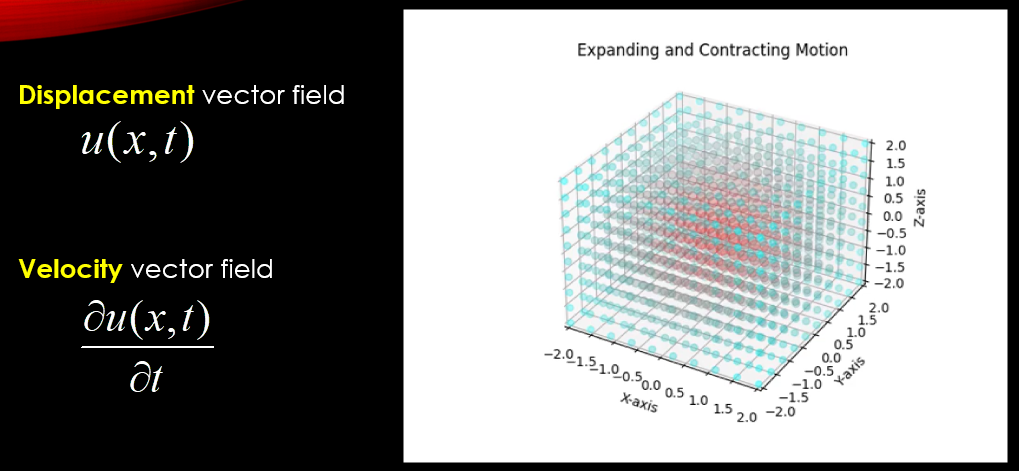
Elastic Waves:
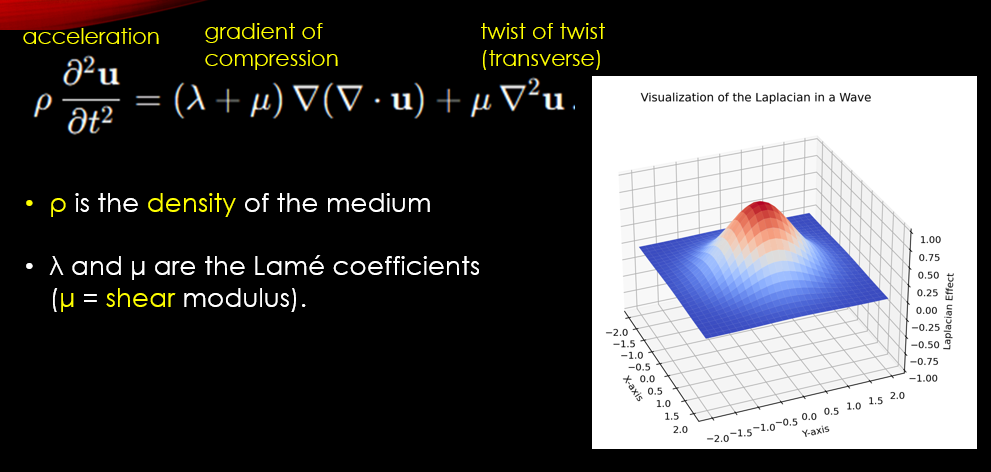
Wave Equation:
Maxwells Ether:
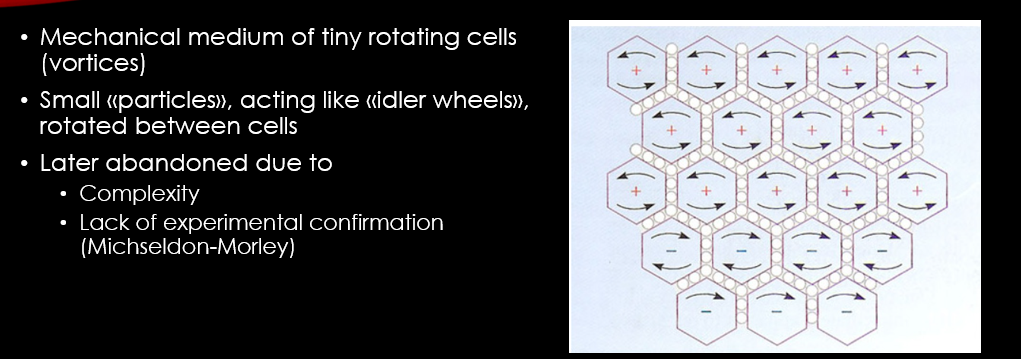
The Restless Universe: Electromagnetism and Fields, Open University
https://www.open.edu/openlearn/science-maths-technology/the-restless-universe/content-section-2.4.1
Electromagnetic Potential:
\[A(x,t) \equiv \frac{{{u_T}(x,t)}}{{\partial t}}\]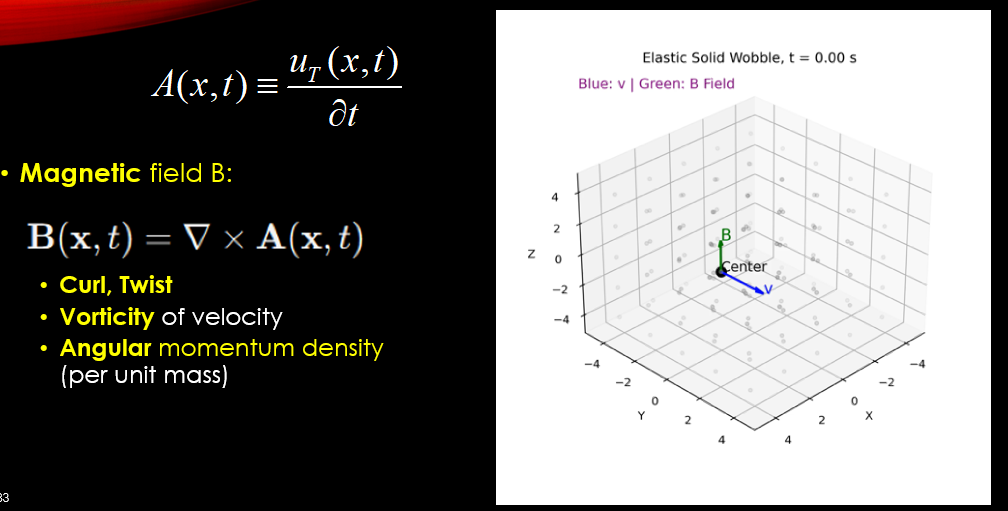
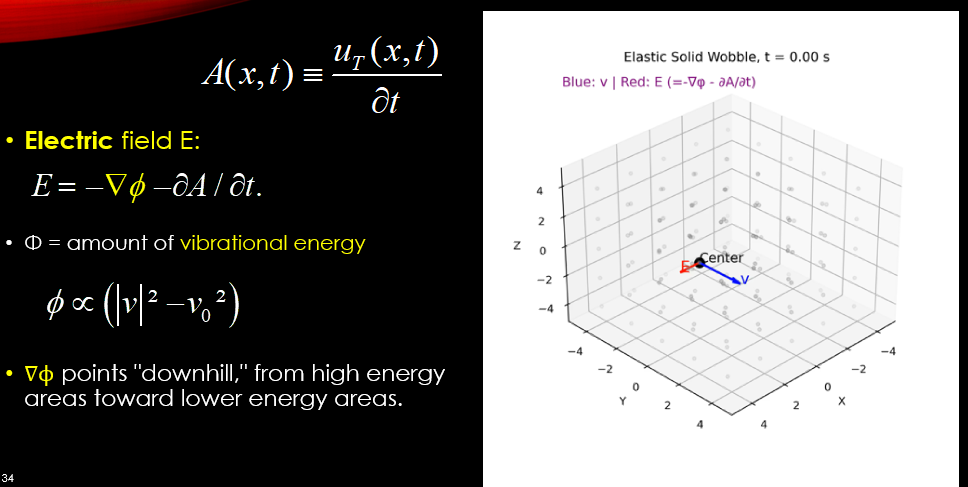
Electric Field E:
\[E\; = \;–\nabla \phi –\;\partial A/\partial t\]•Φ = amount of vibrational energy
\[\phi \propto \left( {\left| v \right|\;–\;{v_0}} \right)\]∇ϕ points “downhill,” from high energy areas toward lower energy areas
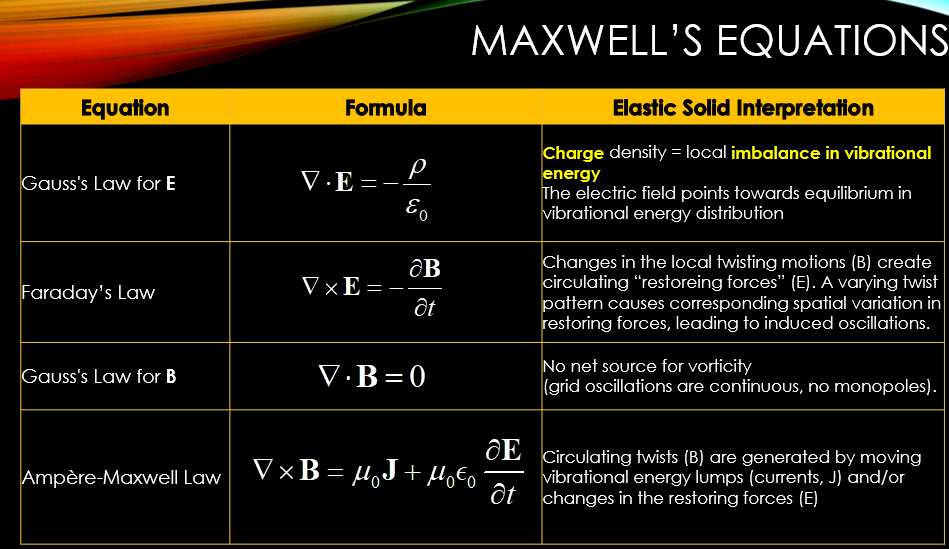
| Equation | Formula | Elastic Solid Interpretation |
| Gauss’s Law for E | Charge density = local imbalance in vibrational energy The electric field points towards equilibrium in vibrational energy distribution | |
| Faraday’s Law | Changes in the local twisting motions (B) create circulating “restoreing forces” (E). A varying twist pattern causes corresponding spatial variation in restoring forces, leading to induced oscillations. | |
| Gauss’s Law for B | No net source for vorticity (grid oscillations are continuous, no monopoles). | |
| Ampère-Maxwell Law | Circulating twists (B) are generated by moving vibrational energy lumps (currents, J) and/or changes in the restoring forces (E) |
Spin 1/2

Double Slit Experiment
https://jsfiddle.net/Chenopdodium/kx0dtp7h
Photoelectric Effect
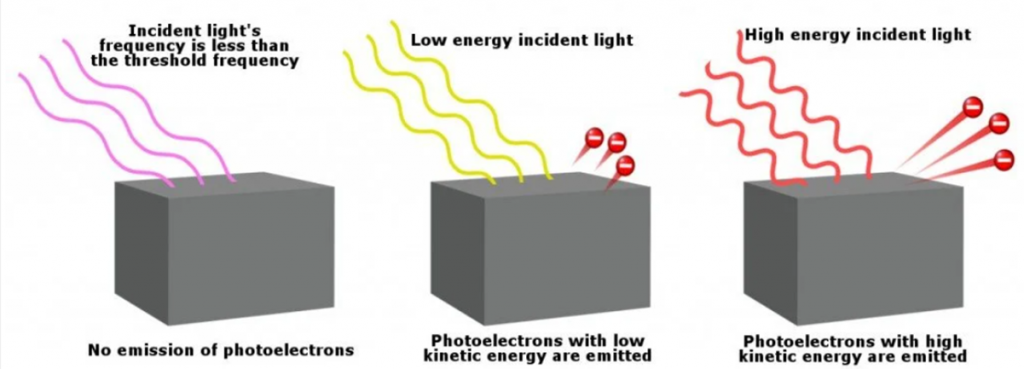
Resonance: https://jsfiddle.net/Chenopdodium/ujsmLf1t/
Photoelectric Effect: https://jsfiddle.net/Chenopdodium/z8bd51of/